What is a Warehouse Management System: All You Need to Know
In the rapidly evolving landscape of supply chain and logistics, efficient warehouse management has become a cornerstone of business success. As companies strive to meet customer expectations and optimize operations, the role of a Warehouse Management System (WMS) has become increasingly vital. This article delves deeply into what a Warehouse Management System is, the key features that make it indispensable, the benefits it offers, and how it is shaping the future of warehousing.

What is a Warehouse Management System (WMS)?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a sophisticated software application designed to support and optimize the day-to-day operations within a warehouse. At its core, a WMS provides a comprehensive solution for managing warehouse resources, including inventory, labor, and equipment. By automating key processes such as inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and warehouse layout optimization, a WMS plays a critical role in improving operational efficiency and reducing costs.

In the context of modern supply chains, a WMS is more than just a tool for managing physical goods. It serves as an integral part of the broader business ecosystem, interfacing with other critical systems like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM). This integration ensures that information flows seamlessly across the organization, enabling real-time decision-making and enhancing overall supply chain visibility. As businesses continue to expand and supply chains grow more complex, the importance of a robust WMS cannot be overstated.
Warehouse Management System Features
A warehousing management system offers a wide array of features designed to streamline warehouse operations and improve overall efficiency. Below are some of the most crucial features that any comprehensive WMS should include:
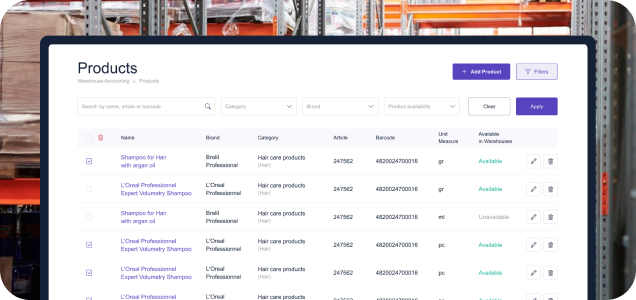
Inventory Management
Inventory management is the backbone of any warehouse operation, and a WMS is designed to handle this task with precision. By providing real-time visibility into inventory levels, a warehouse inventory management system enables businesses to monitor stock movements, track inventory across multiple locations, and ensure that the right products are available when needed.
This real-time capability is particularly valuable in environments with high inventory turnover or seasonal fluctuations. For example, in the retail industry, a WMS can help manage inventory during peak shopping seasons, ensuring that popular items are restocked quickly to meet consumer demand. The system also reduces the risk of overstocking, which can lead to excess inventory costs and wasted storage space.

Order Management
Efficient order management is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction and meeting delivery expectations. A warehouse system management simplifies this process by automating order processing, from picking and packing to shipping and tracking. The system ensures that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time, minimizing the risk of errors and delays.
Order management features within a WMS often include sophisticated algorithms that prioritize orders based on factors such as delivery deadlines, customer importance, and shipping costs. This prioritization helps businesses manage large volumes of orders more effectively, particularly during peak periods. Additionally, a WMS can provide real-time updates on order status, enabling customers to track their shipments and reducing the burden on customer service teams.

Warehouse Layout and Design
The physical layout of a warehouse has a significant impact on operational efficiency. A well-organized warehouse layout minimizes travel time for workers, reduces the likelihood of congestion, and maximizes the use of available space. Warehousing management systems can assist in designing an optimal warehouse layout by analyzing data on inventory movements, order patterns, and storage requirements.
Using this data, the WMS can suggest the most efficient placement of goods within the warehouse. For example, high-turnover items can be positioned near packing stations to reduce picking time, while slower-moving items can be stored in less accessible areas. This strategic arrangement not only improves productivity but also enhances the overall safety of warehouse operations by reducing unnecessary movement and potential hazards.
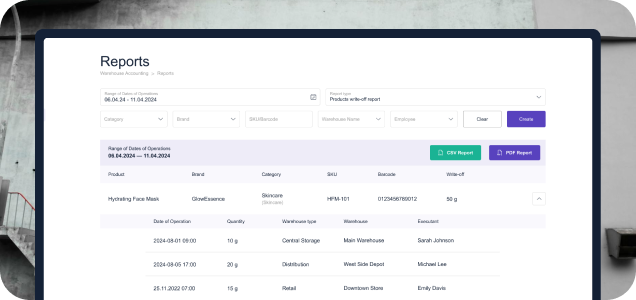
Real-Time Tracking and Reporting
In today’s fast-paced business environment, real-time data is essential for making informed decisions. There is a real-time warehouse management system that gives managers immediate insights into all aspects of warehouse operations. This includes tracking inventory levels, monitoring order status, and analyzing labor productivity.
In real-time, warehouse management system reports allow businesses to identify and address potential issues before they escalate. For example, if a particular product is running low on stock, the system can alert managers to reorder before a stockout occurs. Similarly, if a bottleneck is detected in the picking process, the WMS can suggest adjustments to workflow or staffing levels to alleviate the issue. This level of visibility and control is crucial for maintaining high levels of efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Integration with Other Systems
A warehousing system management must work in harmony with other business systems to deliver maximum value. Integration with ERP systems, for example, allows for the synchronization of financial and operational data, ensuring that inventory costs are accurately reflected in financial reports. Similarly, integration with CRM systems enables businesses to align warehouse operations with customer service goals, such as prioritizing orders for high-value customers.
Seamless integration also facilitates better demand forecasting and inventory planning. By connecting the WMS with sales and marketing data, businesses can anticipate changes in demand and adjust their inventory levels accordingly. This proactive approach helps prevent stockouts and overstock situations, ultimately leading to a more responsive and agile supply chain.
Benefits of a Warehouse Management System
The implementation of a WMS offers numerous benefits that extend beyond the confines of the warehouse. These advantages can have a profound impact on overall business performance and customer satisfaction:

Improved Inventory Accuracy
One of the most significant warehouse management system advantages is the improvement in inventory accuracy. By automating the tracking and management of inventory, a WMS reduces the risk of human error, which is often a major cause of discrepancies in inventory counts. Accurate inventory data is essential for making informed decisions about purchasing, stocking, and order fulfillment.
With a WMS, businesses can maintain a precise record of inventory levels at all times, reducing the likelihood of stockouts or overstocking. This accuracy not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring that products are available when needed. Moreover, accurate inventory data can lead to cost savings by reducing the need for safety stock and minimizing waste due to overstocking.

Enhanced Customer Service
Customer service is a key differentiator in today’s competitive marketplace, and a WMS plays a crucial role in enhancing the customer experience. By streamlining order processing and improving order accuracy, a WMS helps businesses meet delivery deadlines and reduce the likelihood of order errors. These improvements lead to higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
A WMS also provides real-time visibility into order status, allowing businesses to offer more accurate and timely information to customers. This transparency helps build trust with customers and can reduce the volume of inquiries to customer service teams, freeing them up to handle more complex issues.

Increased Efficiency and Productivity
Efficiency and productivity are at the heart of successful warehouse operations, and a WMS delivers on both fronts. By automating routine tasks such as inventory tracking, order processing, and reporting, a WMS frees up warehouse staff to focus on more value-added activities. This automation leads to faster processing times, fewer errors, and ultimately, a more efficient operation.
In addition to automating tasks, a WMS can optimize warehouse workflows by analyzing data on inventory movements, order patterns, and labor productivity. This analysis allows businesses to identify inefficiencies and make adjustments to improve performance. For example, a WMS might suggest reconfiguring the warehouse layout to reduce travel time for pickers or adjusting staffing levels during peak periods to ensure that orders are processed on time.

Reduced Operating Costs
Cost reduction is a critical goal for any business, and a WMS can help achieve this by streamlining operations and reducing waste. By improving inventory accuracy, a WMS reduces the need for safety stock and minimizes the costs associated with overstocking. Additionally, by optimizing warehouse layouts and workflows, a WMS can reduce labor costs by minimizing the time and effort required to complete tasks.
The automation of routine tasks also leads to cost savings by reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing the risk of errors that can result in costly rework or returns. Furthermore, the real-time visibility provided by a WMS allows businesses to make more informed decisions about purchasing, stocking, and order fulfillment, leading to better resource utilization and lower overall costs.
Types of Warehouse Management Systems
When selecting a WMS, it's important to understand the different types available, as each offers distinct advantages depending on the specific needs of your business:

Standalone WMS
A standalone WMS is a specialized system designed exclusively for warehouse management. These systems are typically used by businesses that require advanced warehouse management capabilities but do not need integration with other enterprise systems. Standalone WMS solutions are often more affordable and quicker to implement than integrated systems, making them a good choice for small to medium-sized businesses or those with less complex operations.
However, the lack of integration with other systems can be a limitation for businesses that require a more holistic view of their operations. For example, a standalone WMS might not provide real-time updates to financial or customer service systems, potentially leading to discrepancies or delays in decision-making.

Integrated WMS with ERP
For businesses that require a more comprehensive solution, an integrated WMS with ERP offers a unified platform that connects warehouse management with other critical business functions. This integration allows for seamless data flow between the warehouse and other departments, such as finance, procurement, and sales. As a result, businesses can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and visibility across their entire supply chain.
An integrated WMS with ERP is particularly beneficial for large enterprises or businesses with complex supply chains that require real-time data synchronization across multiple locations or departments. However, these systems can be more expensive and complex to implement, requiring a higher level of IT support and ongoing maintenance.

Cloud-Based WMS
Cloud-based WMS solutions offer flexibility and scalability, making them an attractive option for businesses of all sizes. These systems are hosted on the cloud, allowing users to access the WMS from any location with an internet connection. This remote access capability is particularly valuable for businesses with multiple warehouses or those that require real-time visibility into operations from different geographic locations.
Cloud-based WMS solutions also offer the advantage of automatic updates and lower upfront costs, as there is no need for expensive hardware or IT infrastructure. Additionally, the scalability of cloud-based systems makes them ideal for businesses that expect to grow or experience seasonal fluctuations in demand. However, businesses must consider factors such as data security and reliability when choosing a cloud-based WMS provider.

On-Premise WMS
On-premise WMS solutions are installed locally on a company's servers, offering greater control and customization options. These systems are often preferred by businesses with specific requirements that cannot be met by off-the-shelf solutions. On-premise WMS systems allow for deeper integration with existing IT infrastructure and can be tailored to meet the unique needs of the business.
While on-premise WMS solutions offer greater customization and control, they typically require a larger upfront investment and ongoing maintenance. Businesses must also consider the need for IT support to manage the system, as well as the potential for higher costs associated with software updates and system upgrades.
How to Choose a Warehouse Management System?
Selecting the right WMS is a critical decision that requires careful consideration of several factors. The following guidelines can help businesses make an informed choice:

Assess Your Warehouse Needs
The first step in choosing warehouse management systems (WMS) is to conduct a thorough assessment of your warehouse needs. Consider factors such as the size of your warehouse, the volume of inventory, the complexity of your operations, and any specific challenges you face. This assessment will help you identify the key features and capabilities you need in a WMS.
For example, if your warehouse handles a high volume of orders with tight delivery deadlines, you may prioritize a WMS with advanced order management and real-time tracking capabilities. Alternatively, if your primary challenge is managing a large and diverse inventory, you may focus on a WMS with robust inventory management features.

Consider Scalability and Flexibility
As your business grows, your warehouse management needs will evolve. It’s important to choose a WMS (warehouse management system) that is scalable and flexible enough to accommodate future growth and changes in your operations. Look for a system that can easily adapt to fluctuations in order volume, changes in product lines, and the expansion of warehouse locations.
Scalability is particularly important for businesses that experience seasonal peaks or anticipate significant growth in the coming years. A flexible WMS will allow you to add new features or modules as needed, without requiring a complete system overhaul.

Evaluate Integration Capabilities
Integration with existing business systems is a key consideration when choosing WMS (warehouse management systems). Seamless integration with ERP, CRM, and other enterprise systems ensures that data flows smoothly across your organization, reducing the risk of errors and improving overall efficiency.
When evaluating integration capabilities, consider how well the WMS will work with your current IT infrastructure and whether it supports the necessary data exchange protocols. A well-integrated WMS will enable real-time visibility into your entire supply chain, allowing for more informed decision-making and better coordination between departments.

Check Vendor Support and Training
The successful implementation and use of a WMS depend heavily on the support and training provided by the vendor. It’s essential to choose a vendor that offers comprehensive support services, including technical assistance, user training, and ongoing system updates.
ME-POS is a robust solution that excels in providing flexibility, a user-friendly interface, and comprehensive features that extend beyond warehouse management to include other critical business operations. ME-POS is designed to be adaptable across various industries, such as retail, catering, and car services, making it a versatile option for businesses looking to optimize both their warehouse management and other operational needs.
By picking a warehouse management system by ME-POS, businesses can benefit from extensive vendor support and training, ensuring a smooth implementation and effective use of the system.
Unlock Efficiency
with Me-Pos Warehouse Management

Common Challenges in Warehouse Management and How WMS Helps
Warehouse management is fraught with challenges that can impact efficiency, accuracy, and profitability. Warehousing software and warehouse management systems can help businesses overcome these challenges by providing the tools and insights needed to optimize operations:

Managing High Order Volumes
As businesses grow, they often face the challenge of managing high order volumes, particularly during peak seasons. A WMS helps by automating order processing, prioritizing tasks based on urgency, and optimizing picking routes to ensure that orders are fulfilled quickly and accurately.
For example, during the holiday season, a WMS can streamline the picking and packing processes, enabling businesses to handle a surge in orders without compromising on accuracy or delivery times. By managing high order volumes efficiently, businesses can maintain customer satisfaction and reduce the risk of bottlenecks in the warehouse.

Reducing Picking Errors
Picking errors are a common issue in warehouse operations, leading to incorrect shipments, increased return rates, and dissatisfied customers. A WMS minimizes picking errors by providing real-time instructions to warehouse staff and using barcode scanning technology to verify that the correct items are picked.
The system can also implement quality control measures, such as requiring a second check of picked items before they are packed and shipped. These safeguards help ensure that orders are fulfilled accurately, reducing the likelihood of costly mistakes and enhancing the overall customer experience.

Ensuring Data Accuracy
Accurate data is the foundation of effective warehouse management. A WMS ensures data accuracy by automating data entry processes, reducing the potential for human error, and providing real-time updates on inventory levels, order status, and other critical information.
Accurate data allows businesses to make informed decisions about purchasing, stocking, and order fulfillment. It also helps prevent issues such as stockouts or overstocking, which can have a negative impact on profitability. By maintaining accurate data, a WMS enables businesses to optimize their operations and improve overall efficiency.

Optimizing Warehouse Space
Maximizing the use of available warehouse space is a common challenge, especially as inventory levels fluctuate. A WMS helps optimize warehouse space by analyzing data on inventory movements and suggesting the most efficient placement of goods.
For example, a WMS can recommend placing high-turnover items near the packing stations to reduce travel time for pickers, while slower-moving items can be stored in less accessible areas. This strategic use of space not only improves efficiency but also increases the overall storage capacity of the warehouse, allowing businesses to handle more inventory without the need for additional space.
Future Trends in Warehouse Management Systems
The future of warehouse management is being shaped by several emerging trends and technologies. Understanding these trends can help businesses prepare for the next generation of WMS and stay ahead of the competition:

Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are becoming increasingly prevalent in warehouse operations, offering significant improvements in efficiency and accuracy. Automated picking systems, robotic palletizers, and autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are just a few examples of how these technologies are transforming warehouses.
As automation continues to advance, we can expect to see even more sophisticated systems that can handle a wider range of tasks, from picking and packing to inventory management and order fulfillment. These technologies will enable businesses to:
-
Reduce labor costs
-
Increase throughput
-
Improve overall operational efficiency
By embracing these advancements, businesses can stay competitive and meet the demands of a rapidly changing marketplace.
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are poised to revolutionize warehouse management by enabling more advanced analytics, predictive capabilities, and real-time decision-making. These technologies can help businesses optimize their inventory levels, forecast demand more accurately, and identify trends that might otherwise go unnoticed.
For example, AI-powered WMS can analyze historical sales data to predict future demand, allowing businesses to adjust their inventory levels and avoid stockouts or overstock situations. Machine learning algorithms can also identify patterns in warehouse operations, suggesting improvements that can lead to greater efficiency and productivity.

Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is playing an increasingly important role in warehouse management, providing real-time data on inventory levels, equipment performance, and environmental conditions. IoT devices can monitor and control various aspects of warehouse operations, from tracking the location of goods to monitoring the condition of perishable items.
IoT technology can also be used to automate routine tasks, such as replenishing stock or adjusting climate controls, based on real-time data. By leveraging IoT, businesses can gain greater visibility into their operations, reduce the risk of errors, and improve overall efficiency.

Sustainability and Green Warehousing
As environmental concerns continue to rise, businesses are looking for ways to make their warehouse operations more sustainable. Green warehousing practices, such as energy-efficient lighting, waste reduction, and the use of renewable energy, are becoming more common.
A WMS can help businesses implement and track these initiatives by providing data on energy usage, waste generation, and other environmental factors. By adopting sustainable practices, businesses can:
-
Reduce their environmental impact
-
Lower operating costs
-
Appeal to environmentally conscious consumers
These practices not only contribute to a healthier planet but also align with the growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products and operations.

Conclusion
A Warehouse Management System is an essential tool for businesses looking to optimize their warehouse operations and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced market.
From improving inventory accuracy to enhancing customer service, the benefits of implementing a WMS are significant and far-reaching. As warehouse management continues to evolve, driven by advances in technology and changing customer expectations, businesses that invest in a robust WMS will be well-positioned to succeed.
Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, a WMS can help you streamline your operations, reduce costs, and drive growth in an increasingly complex and competitive environment.
View more
Related Articles
View more